- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- CYCLOPROPYLMETHANOL CAS NO - 2516-33-8
- 7 Chloro Quanalidine
- 2-CHLORO-1-(3-HYDROXYPHENYL) ETHAN-1- ONE
- 3,4-DIHYDROXY-5-NITRO BENZALDEHYDE
- Oxcarbazepine API
- 1-(3-CHLOROPROPYL)-4-(3-CHLOROPHENYL) PIPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- Duloxetine Hydrochloride
- Trichlorocarbanilide Chemical
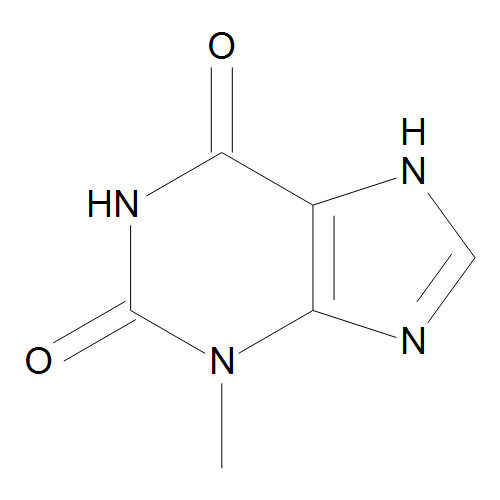
- 3,7-DIMETHYL-1H-PURINE-2,6-DIONE (THEOBROMINE )
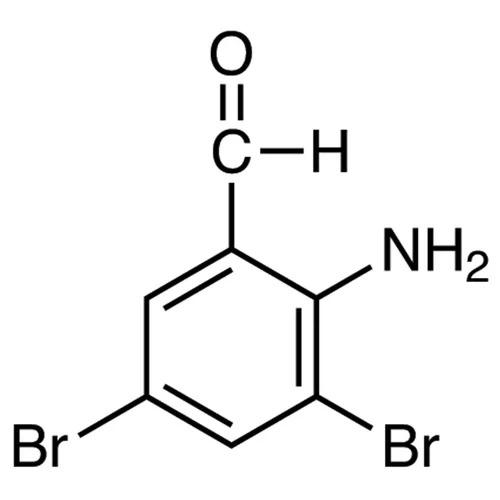
- AMINO,3 5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE
- 2-(2-METHOXY PHENOXY) ETHYLAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- Sertraline Hydrochloride
- Levocetrizine API
- Dompredone API
- Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate
- Carbamazepine API
- 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL-6-(2,4,4-TRIMETHYL PENTYL)-2-(1H)-PYRIDINONE 2-AMINO ETHANOL
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
- Bilastine API
- Ethyl Hexyl Glycerine
- Telmesartan API
- Theobromine API Powder
- Etoricoxib API
- Fluconazole API
- [1,2,4] TRIAZOLO [4,3-A] PYRIDINE-3(2H)-ONE
- Clopidogrel Busulphate
- 2-(2-METHOXY PHENOXY) ETHYL AMINE (BASE)
- 6- CHLORO 2- HEXANONE
- Pharmaceutical Intermediate
- 1-(3-Chlorophenyl) piperazine
- Corey lactone diol
- 6-Chloro-2- Hexanone
- Piroctone Olamine
- Phenylephrine Base
- Ethyl Hexyl Salicylete
- 4-Hydroxy Coumarin
- Diamino Pyrimidine Oxide
- Avobenzone Chemical
- Dibromo Neopentyl Glycol
- 3,4-Dihydroxy 5-Nitrobenzaldehyde
- Chlorhexidine Base
- Ethyl Hexyl Triazone
- (S)-(-)-N,N-Dimethyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl) propanamine
- Ketosulfane Drug
- Homosalate Cosmetic Grade
- 1-3-Chloro Phenyl - 4 -3-Chioro Propyl Piperazine HCL
- 10-Methoxy Imenostilbine
- 2-Amino-3,5-Dibromo Benzaldehyde
- 2 - Ethoxyethyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- Contact Us
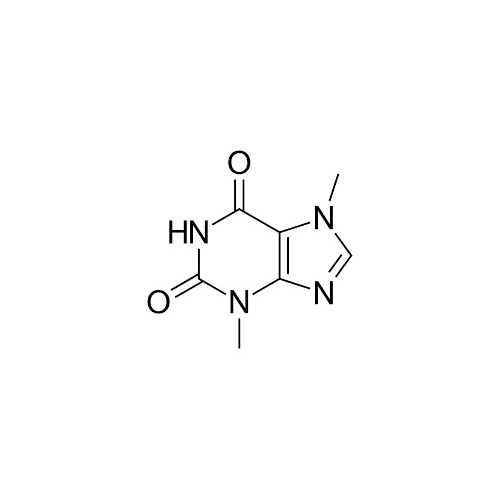
3,7-DIMETHYL-1H-PURINE-2,6-DIONE (THEOBROMINE )
7600 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
X
3,7-DIMETHYL-1H-PURINE-2,6-DIONE (THEOBROMINE ) Price And Quantity
- 1000 Kilograms
- 7600 INR/Kilograms
3,7-DIMETHYL-1H-PURINE-2,6-DIONE (THEOBROMINE ) Trade Information
- Others
- 1000 Kilograms Per Week
- 1 Week
- Yes
- Contact us for information regarding our sample policy
Product Description
37Dimethyl1Hpurine26dione commonly known as Theobromine is a naturally occurring alkaloid of the methylxanthine class It is found primarily in cacao beans tea leaves and other plant sources Heres a detailed overview
Chemical Information
Common Name Theobromine
Chemical Formula C7H8N4O2
Molecular Weight 18016 gmol
Structure
A purine derivative with two ketone groups at the 2nd and 6th positions
Methyl groups attached at the 3rd and 7th positions of the purine ring
Physical Properties
Appearance White crystalline powder
Melting Point Approximately 350C with decomposition
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water
Soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and methanol
Natural Occurrence
Theobromine is most commonly found in
Cacao Beans A primary source making it present in chocolate and cocoa products
Tea Leaves Found in small amounts in black and green tea
Other Plants Found in kola nuts and guarana
Biological Activity
1 Pharmacological Effects
Acts as a mild stimulant similar to caffeine but less potent
Relaxes smooth muscles particularly in the bronchial airways
Functions as a diuretic and vasodilator promoting urine production and widening blood vessels
2 Health Effects
Humans Can have positive effects such as improved mood and focus but excessive consumption may lead to restlessness or insomnia
Animals Toxic to dogs cats and some other animals because they metabolize it much slower than humans
Applications
1 Food Industry
Found in chocolate and cocoabased products as a natural component
2 Pharmaceuticals
Investigated for use in treating asthma due to its bronchodilatory effects
May be studied for its diuretic and cardiac stimulant properties
3 Research
Utilized in studies exploring xanthine derivatives effects on the human body
Safety and Handling
Toxicity
Safe in moderate doses for humans
Can cause theobromine poisoning in animals like dogs if consumed in large amounts eg from chocolate
Handling
Use gloves and goggles during handling in industrial or laboratory settings
Storage
Store in a cool dry place away from light and moisture
Chemical Reactivity
Functional Groups
Ketone groups make it a stable compound under normal conditions
Methyl groups influence its interaction with receptors in the body
Decomposition
Stable at room temperature but may decompose under prolonged heating or exposure to strong acidsbases
Would you like information on its synthesis specific pharmacokinetics or how it compares to caffeine
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry  Send SMS
Send SMS  Call Me Free
Call Me Free 
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese