- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Pharmaceutical Chemical
- 4-Hydroxy Coumarin
- Sodium lauroyl sarcosinate
- 6-Chloro-2- Hexanone
- 10-Methoxy Imenostilbine
- Diamino Pyrimidine Oxide
- Dibromo Neopentyl Glycol
- Ethyl Hexyl Salicylete
- Ethyl Hexyl Triazone
- Piroctone Olamine
- Chlorhexidine Base
- 3,4-Dihydroxy 5-Nitrobenzaldehyde
- 1-3-Chloro Phenyl - 4 -3-Chioro Propyl Piperazine HCL
- Ketosulfane Drug
- Phenylephrine Base
- 2 - Ethoxyethyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Corey lactone diol
- (S)-(-)-N,N-Dimethyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl) propanamine
- Avobenzone Chemical
- Homosalate Cosmetic Grade
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- 2-CHLORO-1-(3-HYDROXYPHENYL) ETHAN-1- ONE
- Ethyl Hexyl Glycerine
- 7 Chloro Quanalidine
- Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate
- Theobromine API Powder
- Trichlorocarbanilide Chemical
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
- Bilastine API
- Duloxetine Hydrochloride
- Levocetrizine API
- Etoricoxib API
- Fluconazole API
- Oxcarbazepine API
- Carbamazepine API
- Telmesartan API
- Dompredone API
- Sertraline Hydrochloride
- Clopidogrel Busulphate
- 7- CHLORO-2-METHYLQUINOLINE
- AMINO,3 5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE
- 3,4-DIHYDROXY-5-NITRO BENZALDEHYDE
- 1-(3-CHLOROPROPYL)-4-(3-CHLOROPHENYL) PIPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- 2-(2-METHOXY PHENOXY) ETHYLAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- 2-(2-METHOXY PHENOXY) ETHYL AMINE (BASE)
- 3,7-DIMETHYL-1H-PURINE-2,6-DIONE (THEOBROMINE )
- 6- CHLORO 2- HEXANONE
- [1,2,4] TRIAZOLO [4,3-A] PYRIDINE-3(2H)-ONE
- 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL-6-(2,4,4-TRIMETHYL PENTYL)-2-(1H)-PYRIDINONE 2-AMINO ETHANOL
- CYCLOPROPYLMETHANOL CAS NO - 2516-33-8
- 1-(3-Chlorophenyl) piperazine
- Pharmaceutical Chemical
- Contact Us
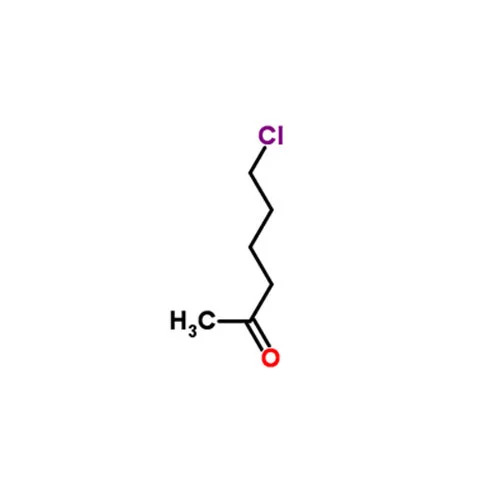
6- CHLORO 2- HEXANONE
6540 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
X
6- CHLORO 2- HEXANONE Price And Quantity
- 6540 INR/Kilograms
- 1000 Kilograms
6- CHLORO 2- HEXANONE Trade Information
- Others
- 1000 Kilograms Per Day
- 1 Week
- Yes
- Contact us for information regarding our sample policy
Product Description
6Chloro2hexanone is an organic compound belonging to the class of haloketones characterized by the presence of a ketone and a chloro substituent Heres a detailed overview
Chemical Information
Chemical Name 6Chloro2hexanone
Chemical Formula C6H11ClO
Molecular Weight 13461 gmol
Structure
Ketone Group CO Positioned at the 2nd carbon of the hexane chain
Chloro Group Cl Attached to the terminal carbon at the 6th position
Physical Properties
Appearance A colorless to pale yellow liquid
Boiling Point Approximately 180200C subject to experimental determination
Density Slightly higher than water due to the chloro substituent
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water
Miscible with many organic solvents such as ethanol diethyl ether and acetone
Applications
1 Chemical Synthesis
Used as an intermediate in organic synthesis especially for creating derivatives with potential applications in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals
The ketone and chloro groups provide versatility in nucleophilic substitution and condensation reactions
2 Research and Development
Commonly used in laboratories for studying reactivity and mechanisms of haloketones
3 Specialty Chemicals
May serve as a precursor for the preparation of polymers resins or other industrial compounds
Reactivity
Ketone Group CO
Highly reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions
Can form enolates under basic conditions making it suitable for aldol condensations or Michael additions
Chloro Group Cl
Reacts with nucleophiles in substitution reactions allowing functional group transformations
Susceptible to elimination reactions under basic conditions potentially forming alkenes
Safety and Handling
Hazards
Can be irritating to the skin eyes and respiratory tract
Vapors may be harmful if inhaled
Handling
Use appropriate personal protective equipment PPE including gloves goggles and lab coats
Work in a wellventilated area or under a fume hood
Storage
Store in a tightly sealed container in a cool dry and ventilated area
Keep away from heat light and incompatible substances like strong oxidizing or reducing agents
Chemical Stability
Thermal Stability Stable under normal laboratory conditions but may degrade under prolonged exposure to heat
Incompatibilities Avoid strong acids bases and oxidizing agents which may induce decomposition or unwanted side reactions
Would you like more information about its synthesis reactions or applications in specific industries
Enter Buying Requirement Details

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry  Send SMS
Send SMS  Call Me Free
Call Me Free 
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese