- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- CYCLOPROPYLMETHANOL CAS NO - 2516-33-8
- 7 Chloro Quanalidine
- 2-CHLORO-1-(3-HYDROXYPHENYL) ETHAN-1- ONE
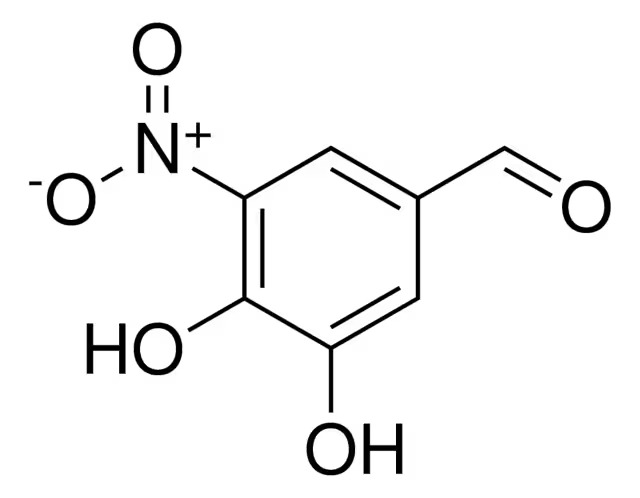
- 3,4-DIHYDROXY-5-NITRO BENZALDEHYDE
- Oxcarbazepine API
- 1-(3-CHLOROPROPYL)-4-(3-CHLOROPHENYL) PIPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- Duloxetine Hydrochloride
- Trichlorocarbanilide Chemical
- 3,7-DIMETHYL-1H-PURINE-2,6-DIONE (THEOBROMINE )
- AMINO,3 5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE
- 2-(2-METHOXY PHENOXY) ETHYLAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
- Sertraline Hydrochloride
- Levocetrizine API
- Dompredone API
- Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate
- Carbamazepine API
- 1-HYDROXY-4-METHYL-6-(2,4,4-TRIMETHYL PENTYL)-2-(1H)-PYRIDINONE 2-AMINO ETHANOL
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
- Bilastine API
- Ethyl Hexyl Glycerine
- Telmesartan API
- Theobromine API Powder
- Etoricoxib API
- Fluconazole API
- [1,2,4] TRIAZOLO [4,3-A] PYRIDINE-3(2H)-ONE
- Clopidogrel Busulphate
- 2-(2-METHOXY PHENOXY) ETHYL AMINE (BASE)
- 6- CHLORO 2- HEXANONE
- Pharmaceutical Intermediate
- 1-(3-Chlorophenyl) piperazine
- Corey lactone diol
- 6-Chloro-2- Hexanone
- Piroctone Olamine
- Phenylephrine Base
- Ethyl Hexyl Salicylete
- 4-Hydroxy Coumarin
- Diamino Pyrimidine Oxide
- Avobenzone Chemical
- Dibromo Neopentyl Glycol
- 3,4-Dihydroxy 5-Nitrobenzaldehyde
- Chlorhexidine Base
- Ethyl Hexyl Triazone
- (S)-(-)-N,N-Dimethyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl) propanamine
- Ketosulfane Drug
- Homosalate Cosmetic Grade
- 1-3-Chloro Phenyl - 4 -3-Chioro Propyl Piperazine HCL
- 10-Methoxy Imenostilbine
- 2-Amino-3,5-Dibromo Benzaldehyde
- 2 - Ethoxyethyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- Contact Us
Fluconazole API
100.0 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
X
Fluconazole API Price And Quantity
- 100.0 INR/Kilograms
- 1000 Kilograms
Product Description
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication belonging to the class of triazole antifungals. It is used to treat various fungal infections caused by Candida species and Cryptococcus neoformans, among others. Here's a detailed description of fluconazole:
Mechanism of Action
Fluconazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. By blocking the enzyme lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, which is involved in the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, fluconazole disrupts fungal cell membrane integrity, leading to fungal cell death.
Indications
1. Vaginal Yeast Infections Fluconazole is commonly prescribed for the treatment of vaginal yeast infections (vaginal candidiasis). It effectively relieves symptoms such as itching, burning, and discharge associated with this condition.
2. Oropharyngeal and Esophageal Candidiasis Fluconazole is used to treat oral thrush (oropharyngeal candidiasis) and esophageal candidiasis, which are fungal infections affecting the mouth and throat.
3. Systemic Candidiasis In severe cases, where the infection has spread beyond the mucosal surfaces, fluconazole is used to treat systemic candidiasis, including candidemia, disseminated candidiasis, and invasive candidiasis.
4. Cryptococcal Meningitis Fluconazole is an effective treatment option for cryptococcal meningitis, a fungal infection of the central nervous system caused by Cryptococcus neoformans.
5. Prophylaxis Fluconazole may be used for prophylaxis to prevent fungal infections in patients with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplantation, or with HIV/AIDS.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of fluconazole varies depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection, as well as individual patient factors such as age, weight, and renal function. It is available in oral tablet, oral suspension, and intravenous (IV) forms. The typical dose ranges from 50 mg to 400 mg once daily, with treatment durations varying from a single dose to several weeks or longer.
Adverse Effects
Common side effects of fluconazole include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, and rash. Rare but serious adverse effects may include liver toxicity, allergic reactions, and severe skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. Fluconazole may also interact with other medications, particularly those metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system.
Precautions
- Fluconazole should be used with caution in patients with liver disease, impaired renal function, or certain cardiac conditions.
- It should be avoided in pregnancy unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks, as it may harm the unborn baby.
- Caution is advised when prescribing fluconazole to breastfeeding mothers, as small amounts of the drug may pass into breast milk.
- Patients should be monitored for signs of liver dysfunction and other adverse effects during treatment with fluconazole.
Conclusion
Fluconazole is a widely used antifungal medication with broad-spectrum activity against various fungal pathogens. It is an important tool in the management of fungal infections, offering efficacy, convenience, and generally favorable tolerability when used appropriately under medical supervision. However, like all medications, fluconazole carries risks of adverse effects and interactions, and its use should be guided by healthcare professionals based on individual patient needs and circumstances.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry  Send SMS
Send SMS  Call Me Free
Call Me Free 
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese